This article investigates the effect of TiC content on the microstructure and wear resistance of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy cladding layer. AlCoCrFeNi 2xMo xTiC (x=0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.4) alloy cladding layers were prepared on the surface of 40CrNiMo steel by laser cladding technology, and the effects of TiC and Mo content on the properties of the cladding layer were analyzed using XRD, SEM, EBSD, TEM, and wear resistance tests.
Experimental Materials and Methods
The substrate is 40CrNiMo steel, and the cladding material is AlCoCrFeNi pre alloyed powder with a particle size of 15-53 μ m.
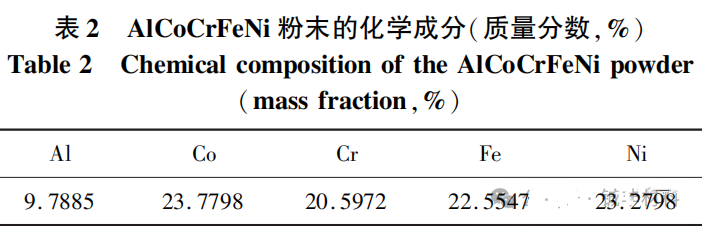
AlCoCrFeNi-2xMo-xTiC alloys were prepared by adding pure Ti powder and Mo ₂ C, with x values of 0.1, 0.25, and 0.4, respectively.
Experimental results and analysis
1.Microstructure analysis
The fusion layer forms a metallurgical bond with the substrate, without cracks or pores. As the TiC content increases, the size of the precipitated phase gradually increases and the morphology changes from fishbone to circular.
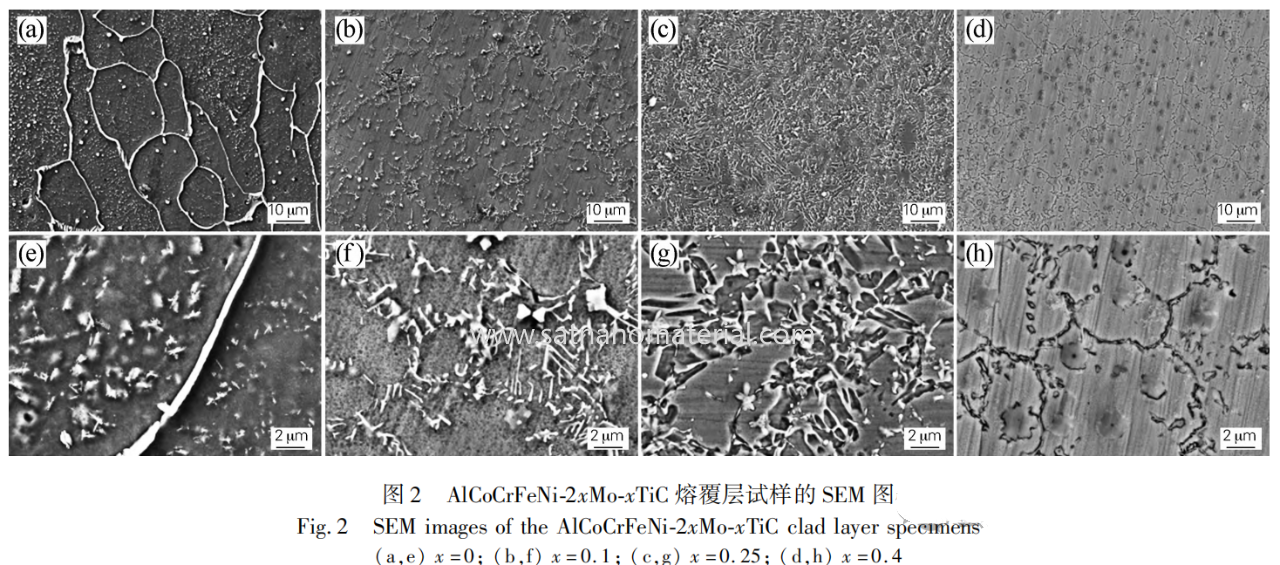
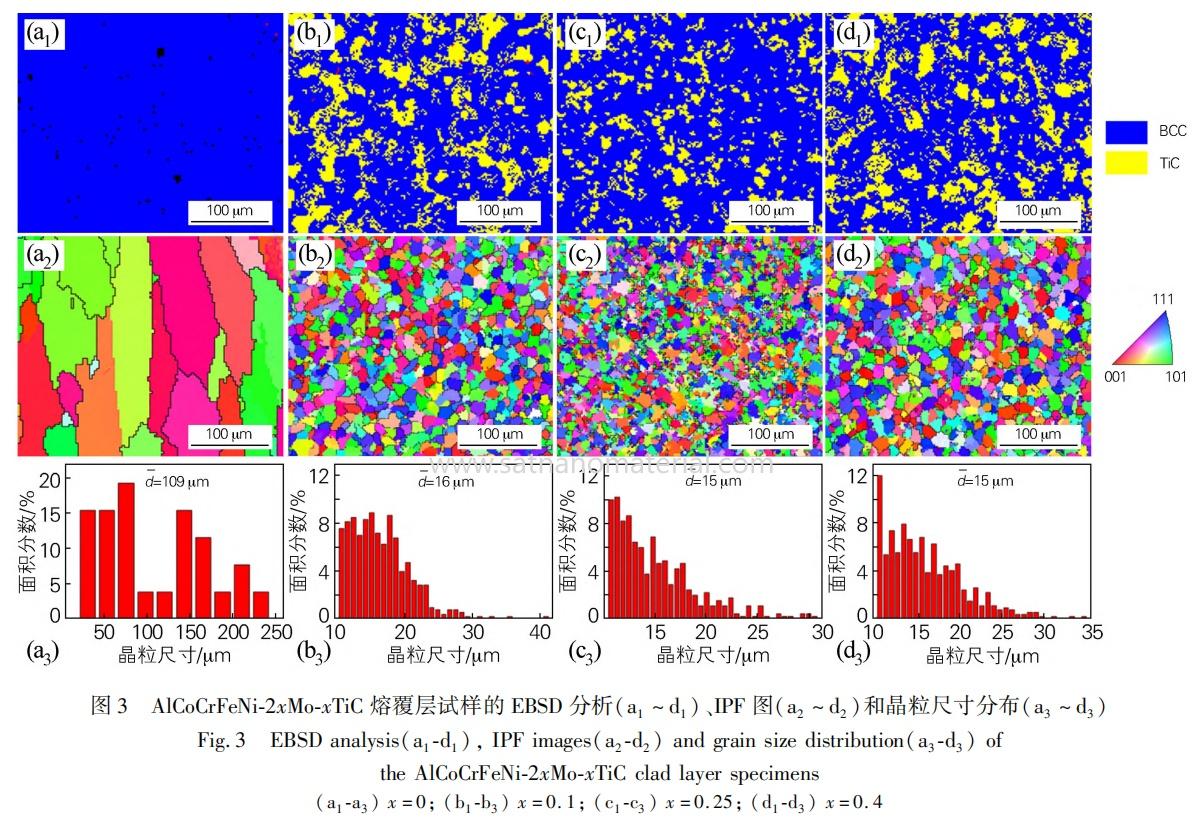
The AlCoCrFeNi cladding layer is mainly composed of coarse columnar crystals, while the addition of TiC significantly refines the grain size, reducing it from 109 μ m to 15 μ m. TiC, as a heterogeneous nucleation site, inhibits grain growth. The cladding layer is composed of BCC and TiC phases, and the addition of TiC significantly refines the grain size and improves the uniformity of the microstructure.
2.mechanical properties
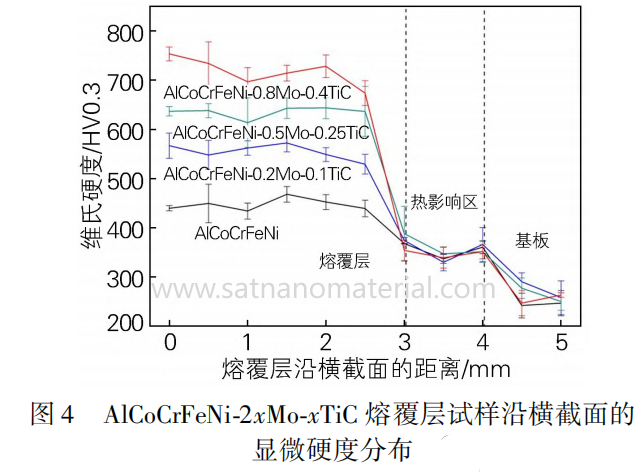
As the TiC content increases, the hardness of the cladding layer gradually increases. The hardness of AlCoCrFeNi-0.8Mo-0.4TiC is the highest, reaching 750HV0.3, which is 300HV0.3 higher than that of AlCoCrFeNi without TiC added.
3.wear resistance
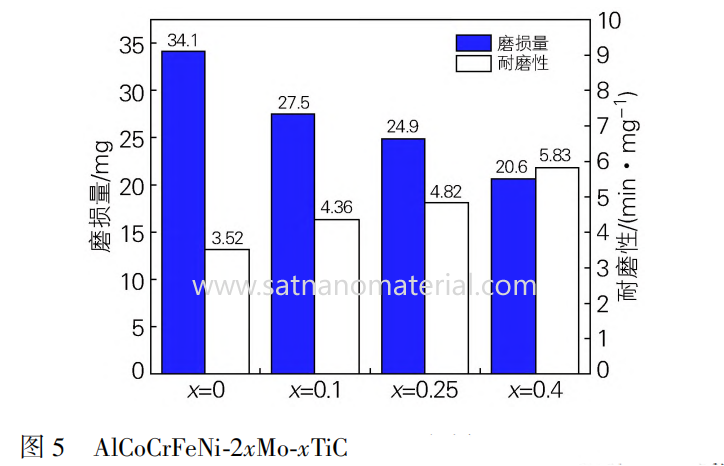
The wear amount decreases with the increase of TiC content. AlCoCrFeNi-0.8Mo-0.4TiC has the smallest wear amount and the best wear resistance. The wear mechanism shifts from adhesive wear (AlCoCrFeNi) to abrasive wear (sample with TiC added)
4. Corrosion mechanism
The AlCoCrFeNi cladding layer has a low hardness and a large amount of wear debris on the worn surface, mainly due to adhesive wear. After adding TiC, the hardness of the cladding layer significantly increased, and shallow grooves and a small amount of debris appeared on the worn surface. The wear mechanism is abrasive wear. TiC particles have good adhesion with the matrix and no peeling phenomenon has occurred.
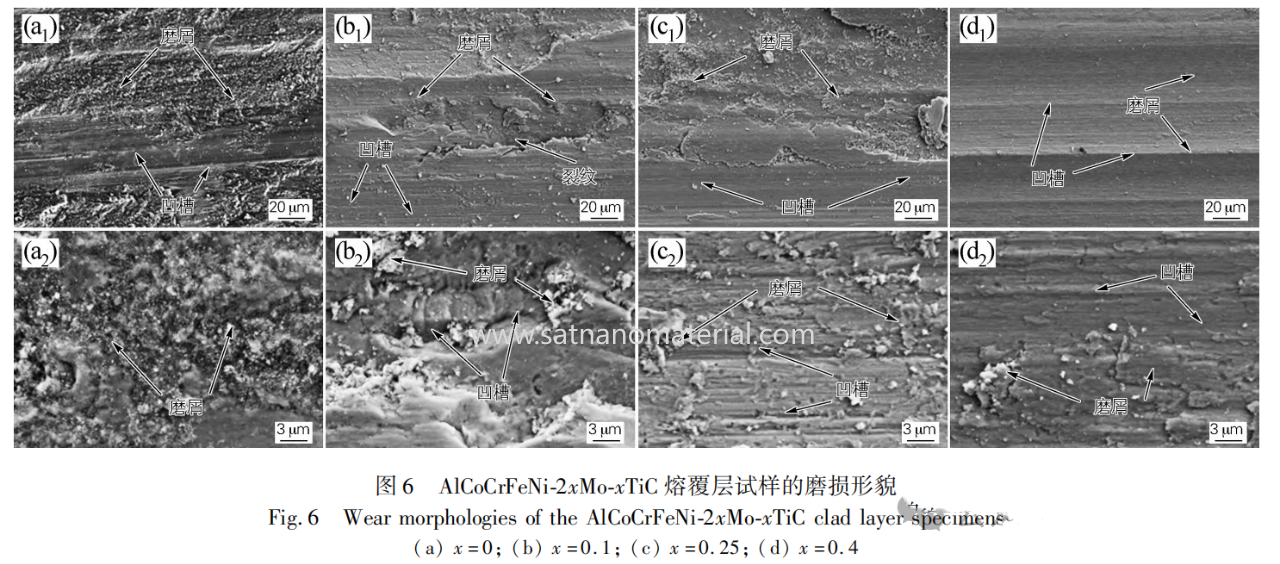

conclusion
The AlCoCrFeNi-2xMo-xTiC cladding layer is composed of BCC and TiC phases, and the addition of TiC significantly refines the grain size, reducing it from 109 μ m to 15 μ m. The AlCoCrFeNi-0.8Mo-0.4TiC cladding layer has the highest hardness (750HV0.3) and the best wear resistance. The addition of TiC significantly improves the hardness and wear resistance of the cladding layer. The AlCoCrFeNi cladding layer without TiC addition is mainly characterized by adhesive wear, while the wear mechanism changes to abrasive wear after TiC addition, and TiC particles have good bonding with the matrix.
SAT NANO is a best supplier of alloy powder and metal powder in China, we can offer Ti powder and AlCoCrFeNi alloy powder, we also can supply carbide powder like TiC powder, if you have any enquiry, please feel free to contact us at admin@satnano.com
 online service
online service 13929258449
13929258449 admin@satnano.com
admin@satnano.com + 8613929258449
+ 8613929258449