1.2 Composition Change Solid Solution Formation: Doping, alloying, or ion substitution (such as Co ² ⁺ replacing Fe ² ⁺) can alter the lattice constant. The following is the XRD analysis of Cu doped NCM:
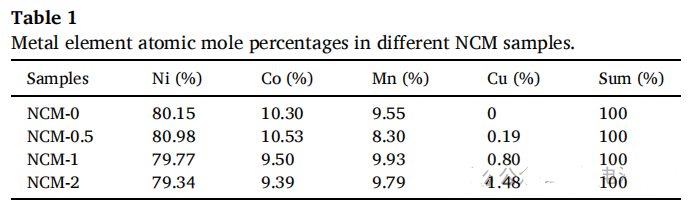
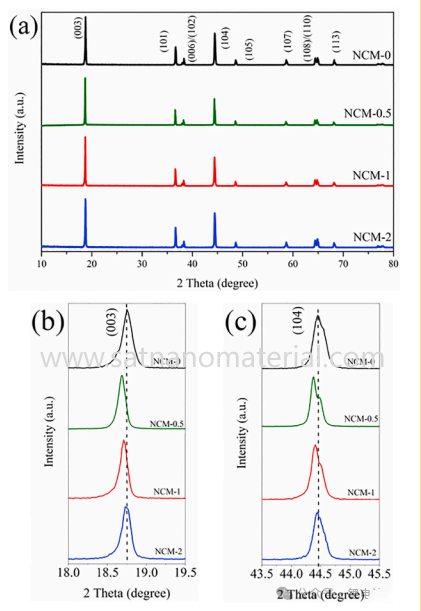
(a) XRD patterns of synthesized materials, and selected insets of peaks (b) (003) and (c) (004)
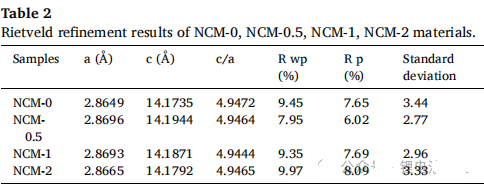
It can be seen that the parameter of lattice NCM-0 is the smallest among all samples. When the content of Cu is 0.5%, the peaks of (003) and (104) shift towards lower directions due to the larger radius of Cu2+. As the Cu content gradually increases, Ni2+(0.069 nm) oxidizes to Ni3+(0.056 nm), resulting in lattice shrinkage.
If the solute atom radius is larger than the solvent atom → lattice expansion → peak position shifts towards lower angles. On the contrary, the lattice shrinks and the peak position shifts towards higher angles. Non stoichiometric ratio: When the composition of oxides (Fe ∝ O ₄ vs. FeO) or sulfides deviates from the stoichiometric ratio, changes in lattice parameters lead to peak shift.
1.3 Temperature effect thermal expansion/contraction: When tested at high or low temperatures, the lattice constant changes due to thermal expansion, resulting in peak shift (high temperature → lattice expansion → low angle shift). Therefore, the XRD testing room should maintain stable temperature and humidity.
Phase transition: Temperature changes may induce phase transitions (such as tetragonal phase → cubic phase), resulting in significant peak shifts or the appearance of new peaks.
1.4 Preferred orientation (texture)
If there is a preferred orientation during the sample preparation process, it may lead to abnormal diffraction intensity of certain crystal planes, but it usually does not affect the peak position. If the orientation difference leads to lattice distortion (such as strain in thin films), it may indirectly cause peak shift.
2. Instrument and experimental conditions factors
2.1 Zero point calibration error of the angle measuring instrument: Failure to calibrate the zero point of the angle measuring instrument will result in overall displacement of all diffraction peaks (systematic error), which needs to be calibrated with a standard sample (such as silicon powder).
2.2 Sample placement deviation: The surface of the sample is not aligned with the axis of the angle measuring instrument (such as height deviation or tilt), which can cause peak position deviation. This can be solved by optimizing the sample loading.
2.3 When using different target materials (such as Cu K α vs. Co K α), the wavelength difference of the X-ray source will cause an overall shift in peak position (according to the Bragg equation). Need to confirm if the test parameters are consistent.
2.4 Scanning mode or parameter settings errors. Improper parameter settings for continuous scanning mode and step scanning mode (such as scanning speed and step size) may cause slight peak shift, but usually affect peak shape more than peak position.
3. Sample preparation issues: Excessive grinding: Mechanical grinding may introduce strain or nanocrystallization, resulting in peak shift or broadening. Non uniformity: Uneven composition or thickness may lead to differences in local peak positions. Surface pollution or oxidation: Surface oxidation or pollution may produce additional phases that overlap with the original peak, resulting in apparent shift.
4. Data analysis error peak finding algorithm error: If the background is not properly subtracted or noise interference occurs during automatic peak finding, the peak position may be misjudged. Instrument broadening effect: If the instrument broadening function is not calibrated, it may lead to peak fitting deviation.
The core reason for XRD peak shift is the variation in interplanar spacing (d value), which may be due to internal factors (stress, composition, phase transition) or external factors (instrument errors, preparation issues) of the sample. Comprehensive analysis should be conducted based on experimental conditions, sample history, and auxiliary characterization methods.
SAT NANO is the best supplier of nanopowder and micro powder in China, we can offer metal powder, ,alloy powder and oxide powder and carbide powder, if you have any enquiry, please feel free to contact us at admin@satnano.com
 online service
online service 13929258449
13929258449 admin@satnano.com
admin@satnano.com + 8613929258449
+ 8613929258449