CAS 7440-05-3 Pd nanopowder Ultrafine Palladium as catalyst
Size:20-30nm Purity:99.95% CAS No:7440-05-3 ENINEC No.:231-115-6 Appearance:black Powder Shape:spherical
Size:20-30nm Purity:99.95% CAS No:7440-05-3 ENINEC No.:231-115-6 Appearance:black Powder Shape:spherical
We can supply different size products of niobium silicide powder according to client's requirements. Size:1-3um; Purity:99.5%;Shape:granular CAS No:12034-80-9;ENINEC No.:234-812-3
Ni2Si particle,99.5% purity,granular shape,is used for Microelectronic integrated circuit, nickel silicide film,etc. Size:1-10um; CAS No:12059-14-2;ENINEC No.:235-033-1
Recently, Professor Xie Tao and Associate Researcher Wu Jingjun's team from the School of Chemical Engineering and Bioengineering at Zhejiang University published an article titled "3D printable elastomers with exceptional strength and toughness" in Nature. The study reported a 3D photo printed resin chemistry that produced elastomers with a tensile strength of 94.6 MPa and a toughness of 310.4 MJ m-3, far exceeding any 3D printed elastomer. Mechanically speaking, this is achieved by printing dynamic covalent bonds in polymers, allowing for network topology reconfiguration and facilitating the formation of hierarchical hydrogen bonds (especially amide hydrogen bonds), microphase separation, and interpenetrating structures, thereby synergistically promoting excellent mechanical properties. This work provides a brighter future for large-scale manufacturing using 3D printing.
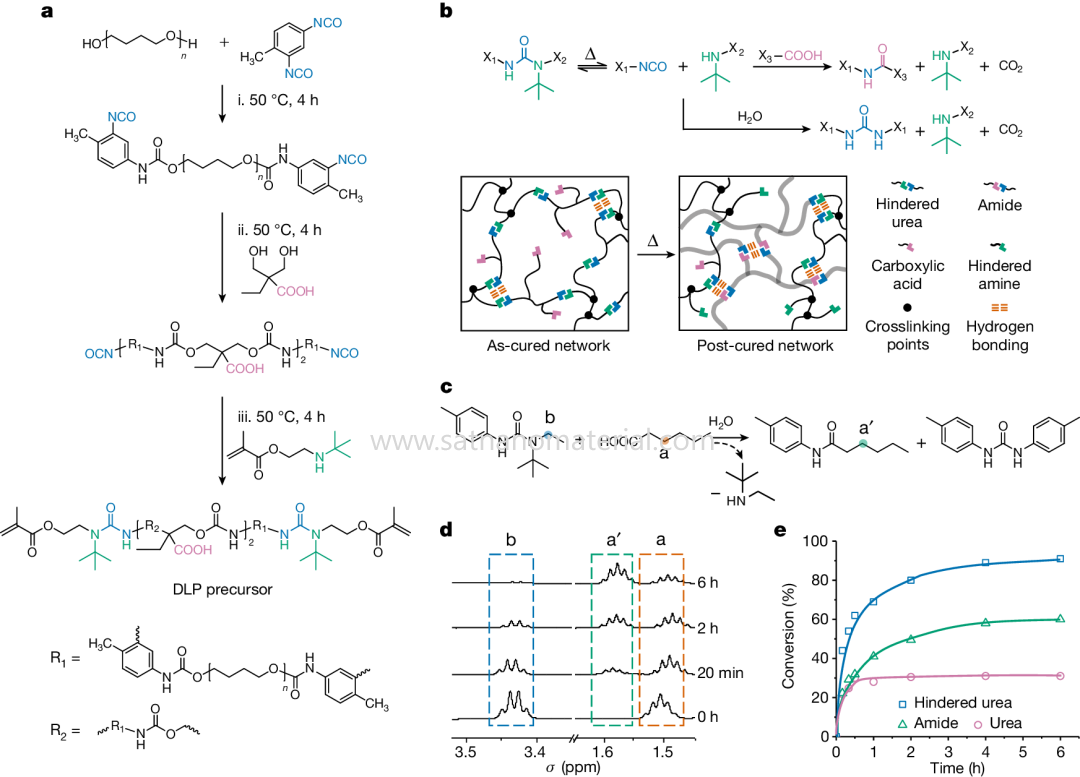
Figure 1: Chemical Design of 3D Photoprinted Elastomers © 2024 Springer Nature
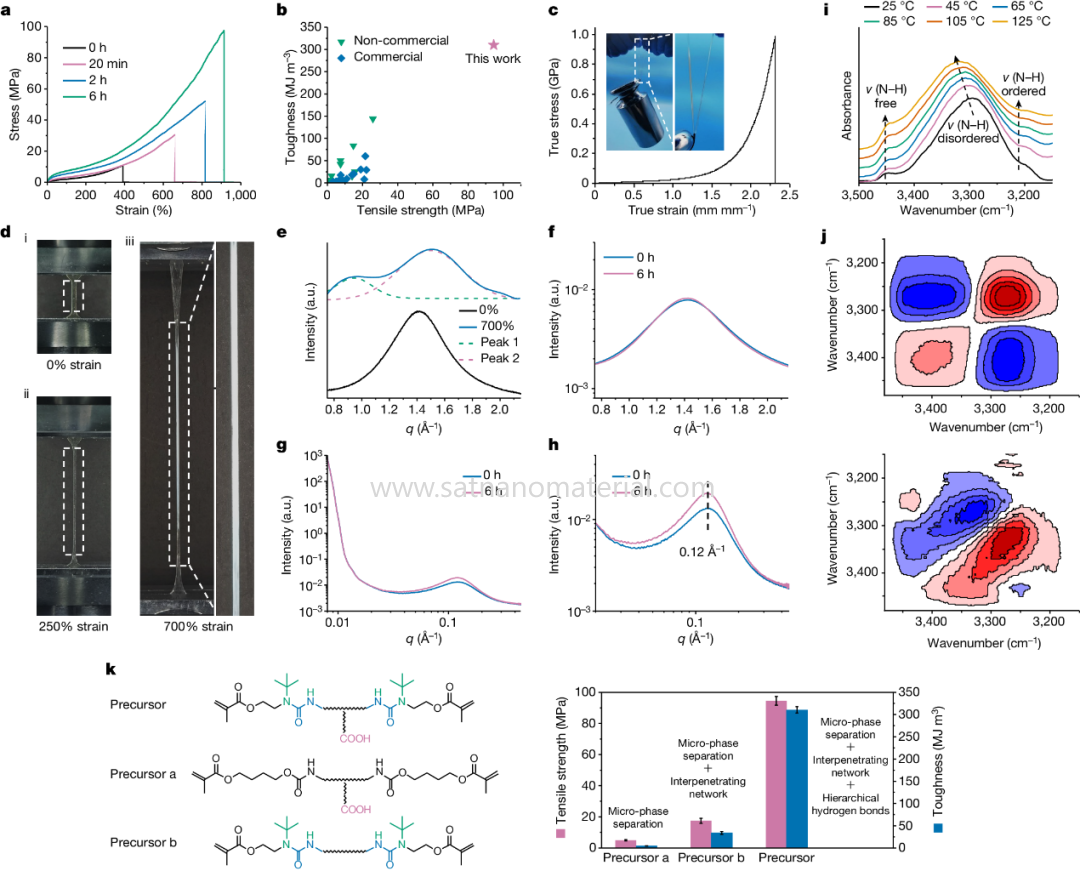
Figure 2. Mechanical properties of elastomers and their strengthening and toughening mechanisms © 2024 Springer Nature
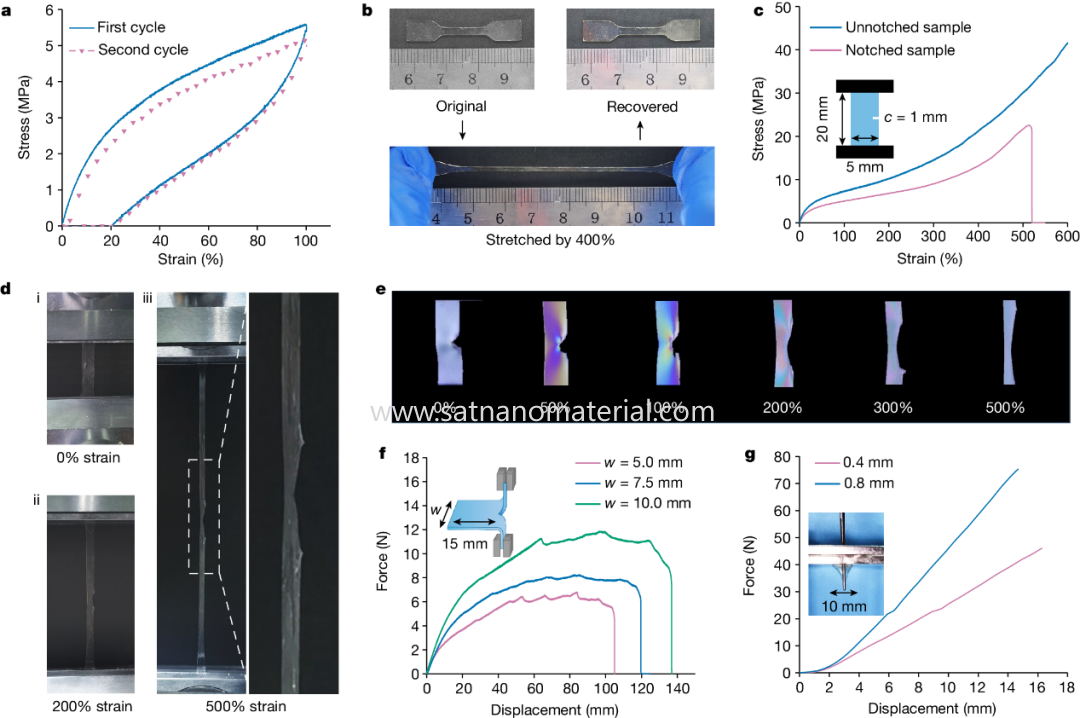
Figure 3. Elasticity and mechanical properties of elastomers © 2024 Springer Nature
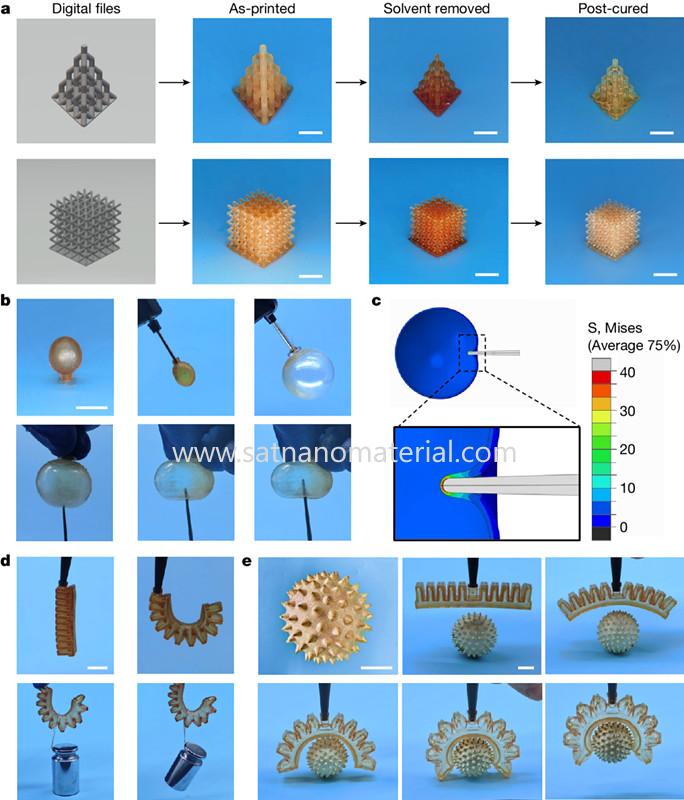
Figure 4: Strong and tough elastomers printed by DLP © 2024 Springer Nature
The ability to 3D print super strong and ultra tough materials in this work extends its range of use under extremely harsh conditions, far beyond the two examples presented in the article. In addition, the printing precursor in this work was synthesized using readily available reagents in simple steps, ensuring its low cost. Although there are other established principles for designing polymers with superior mechanical properties, it is challenging to directly apply them to 3D printing because of the strict requirements for photo printing, including rapid gel under light and sufficient container life during printing and storage. Nevertheless, they provide useful insights for the future development of alternative high-performance 3D printing materials. Overall, the study suggests that 3D printing does not necessarily compromise mechanical performance, which clears a major obstacle for its future commercial implementation.
SAT NANO is a best supplier of metal powder and alloy powder for 3D printing, we also can supply 3D service, if you have any enquiry, please feel free to contact us at admin@satnano.com
 online service
online service 13929258449
13929258449 admin@satnano.com
admin@satnano.com + 8613929258449
+ 8613929258449